I.C. Brindle SOLAS Fire Training Manual 4th Edition: Navigating the Latest SOLAS Fire Regulations & Compliance

The 4th Edition of the SOLAS Fire Training Manual
The maritime industry is continually evolving, with regulations and safety standards regularly updated to address emerging challenges and technological advancements. One such critical area of focus is fire safety, governed by the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS).
The latest amendments and revisions to SOLAS regulations, particularly in the realm of fire safety, have significant implications for maritime operators worldwide. This article provides an overview of the historical context of SOLAS standards, alongside the latest SOLAS regulations, with focus on the updates outlined in the latest I.C. Brindle Fire Safety publication—the 4th Edition of the SOLAS Fire Training Manual (2024).
So, let's dive in...


SOLAS and Maritime Administrations
The SOLAS Convention, 1974, as Amended and Fire Safety
The SOLAS Convention, in its various iterations, holds high importance among international treaties concerning merchant ship safety. Initially adopted in 1914 following the Titanic disaster, subsequent versions were ratified in 1929, 1948, and 1960. The 1974 version, notable for introducing the tacit acceptance procedure, underwent numerous updates and amendments, leading to its current designation as SOLAS, 1974, as amended. This iterative process reflects ongoing efforts to enhance maritime safety standards in response to evolving challenges and technological advancements—including fire protection and fire-stopping aboard vessels.
The primary objective of the SOLAS Convention is to establish minimum standards for the construction, equipment, and operation of ships, ensuring compatibility with safety regulations. Flag States bear the responsibility of ensuring that vessels flying their flag adhere to these requirements, with various certificates mandated by the Convention serving as evidence of compliance. Additionally, the Convention empowers Contracting Governments to conduct inspections of ships from other Contracting States, known as port State control, if there are reasonable grounds to suspect non-compliance with SOLAS standards.
The current SOLAS Convention comprises general obligations, amendment procedures, and other articles, followed by an Annex organised into 14 Chapters, delineating specific safety provisions and regulations. Here they all are laid out:
SOLAS-Compliant Standards in 2024
- General Provisions: Covers ship surveys, issuance of compliance documents, and port State control.
- Construction (Subdivision and Stability, Machinery, and Electrical Installations): Sets standards for ship subdivision, stability, and machinery to ensure safety.
- Fire Protection, Detection, and Extinction: Includes fire safety provisions for all ships and specific measures for different ship types.*
- Life-Saving Appliances and Arrangements: Requirements for life-saving equipment and arrangements, such as lifeboats and life jackets.
- Radiocommunications: Incorporates the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) for improved rescue operations.
- Safety of Navigation: Identifies navigation safety services and operational provisions applicable to all ships.
- Carriage of Cargoes: Covers stowage and securing requirements for various cargo types, including grain carriage.
- Carriage of Dangerous Goods: Regulations for the safe transport of dangerous goods, including documentation and stowage requirements.
- Management for the Safe Operation of Ships: Makes the International Safety Management (ISM) Code mandatory for establishing safety management systems.
- Safety Measures for High-Speed Craft: Mandates compliance with the International Code of Safety for High-Speed Craft (HSC Code).
- Special Measures to Enhance Maritime Safety: Clarifies requirements for recognised organisations, enhanced surveys, and port State control.
- Special Measures to Enhance Maritime Security: Enshrines the International Ship and Port Facilities Security Code (ISPS Code) for maritime security.
- Additional Safety Measures for Bulk Carriers: Includes structural requirements for bulk carriers over 150 meters in length.
- Verification of Compliance: Mandates the IMO Member State Audit Scheme for verifying compliance with SOLAS requirements.
- Safety Measures for Ships Carrying Industrial Personnel: Addresses safety standards for ships transporting industrial personnel engaged in offshore activities.
Of course, we are bringing focus to the fire safety aspects of these SOLAS developments (*highlighted in the section above*), as this relates to our latest release of the Fire Training Manual (4th Edition, 2024).
Over the years, the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has played a leading role in the development and enhancement of fire safety standards within the maritime industry. Beginning with the 1914 SOLAS Convention, which introduced the initial fire protection requirements for international shipping in response to the tragic sinking of the Titanic, IMO has continually worked towards refining and strengthening these standards.
With each subsequent iteration of the SOLAS Convention, spanning from 1929 to 1974, IMO progressively addressed the evolving challenges and lessons learned regarding fire safety at sea. These conventions not only reinforced the importance of fire prevention and suppression measures but also underscored the need for comprehensive regulations applicable to both passenger and cargo vessels.
Throughout the decades, pivotal incidents such as the Morro Castle fire in 1934 and the Scandinavian Star fire in 1990 prompted critical reflections and revisions within IMO's regulatory framework. These incidents led to significant amendments and comprehensive sets of fire safety regulations, highlighting IMO's commitment to continuous improvement in maritime fire safety.
Key developments include the separation of fire safety requirements into dedicated chapters, the establishment of non-combustible construction regulations, and the introduction of advanced fire detection and extinguishing systems. Moreover, the creation of codes such as the International Fire Safety Systems (FSS) Code and the International Code for Application of Fire Test Procedures (FTP Code) further standardised fire safety practices and testing procedures across the industry.
SOLAS Fire Safety: Construction – Fire Protection, Fire Detection and Fire Extingtion
Fire poses a significant threat to ships, especially passenger vessels and those transporting flammable cargo, endangering lives, crew members, and port facilities. On July 1, 2002, revised regulations under SOLAS Chapter II-2 came into effect, incorporating technological advancements and lessons learned from past incidents. These regulations aim to prevent fires through strict control of materials, ensure rapid detection, and facilitate containment and extinguishment. Emphasis is placed on designing ships with clear evacuation routes for the safety of crew and passengers - (IMO, 2019)
The International Maritime Organisation's efforts in promoting fire safety have not only focused on regulatory compliance but also emphasised training, drills, and maintenance practices to enhance operational readiness and crew preparedness in the event of a fire emergency. Additionally, the inclusion of human element considerations in fire safety regulations reflects IMO's holistic approach towards addressing maritime safety challenges.
IMO's commitment to enhancing maritime fire safety standards is evident through its continuous development and refinement efforts. The organisation remains at the forefront of promoting effective fire safety measures worldwide by adapting to technological advancements, incorporating lessons learned from past incidents, and fostering international collaboration.
With the ever-evolving nature of the maritime industry, including technological advancements and the lessons learned from past incidents, IMO consistently adapts its regulations to address emerging challenges and ensure the effectiveness of fire safety measures.
However, it is important to note that this dynamic environment necessitates a constant need for stakeholders within the maritime industry to remain up to date with rapidly changing regulations and best practices.
Whether it's for ensuring compliance during surveyor checks, maintaining peace of mind regarding safety protocols, or fostering a culture of continuous improvement, staying up to date with such fast-changing regualtions and maritime safety standards is paramount. For example, the ability to access and understand the latest updates in fire safety standards not only enhances operational efficiency but also minimises the risk of non-compliance and potential safety hazards.
Additionally, it enables stakeholders to proactively implement necessary measures to safeguard crew members, passengers, and valuable maritime assets. Therefore, facilitating access to comprehensive resources and training materials becomes crucial in empowering stakeholders to navigate the complexities of maritime regulations and uphold the highest standards of safety and security.
Latest Updates to SOLAS Fire Regulations in 4th Edition
In light of the continuous evolution of maritime fire safety standards, our commitment to producing new editions of the Fire Training Manual remains steadfast in 2024 and beyond.
By providing our customers with access to the latest practices and information in maritime fire safety, we empower them to navigate the complex regulatory landscape and uphold the highest standards of safety and security aboard their vessels. Our dedication to keeping pace with regulatory developments underscores our commitment to serving the needs of our customers and promoting a culture of safety excellence within the maritime industry.
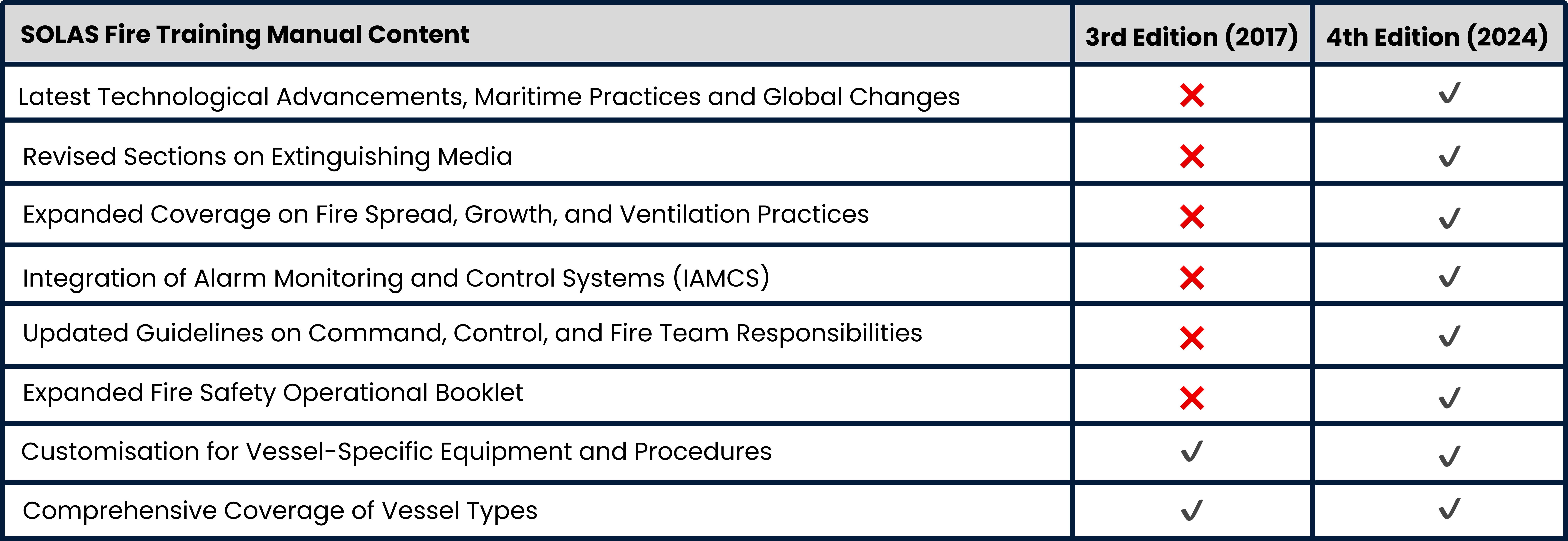
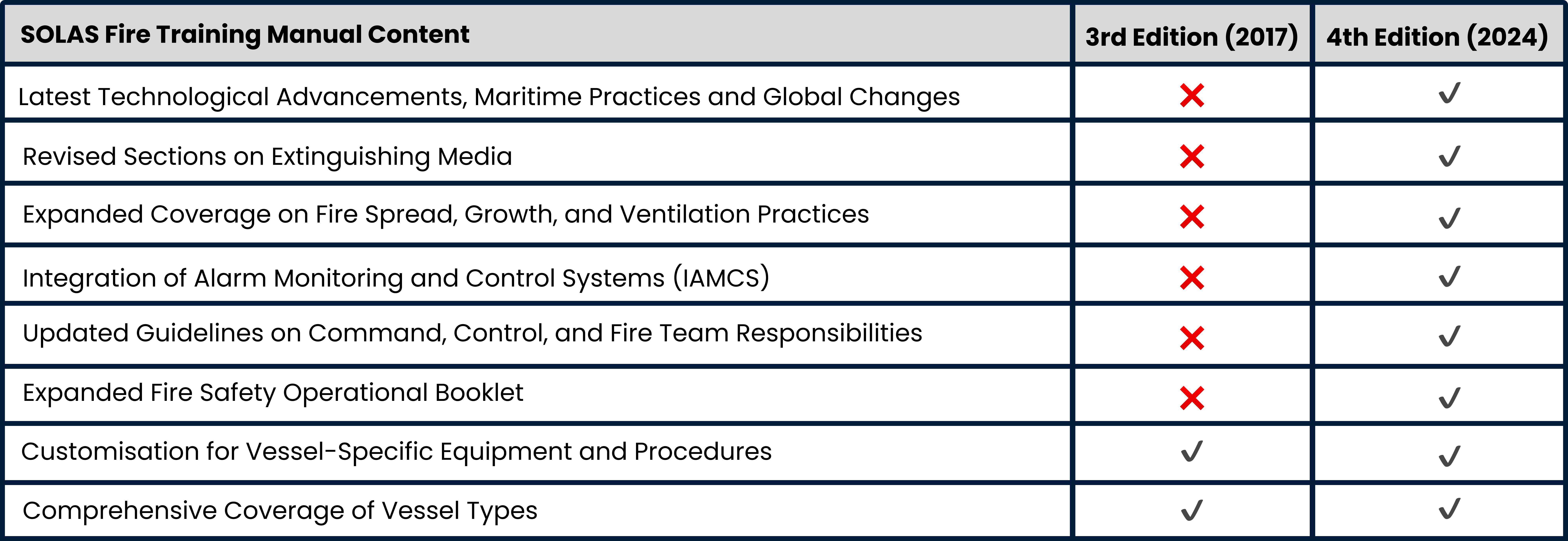
The 4th Edition of the SOLAS Fire Training Manual (2024) reflects the most recent advancements in technology, shipping practices, and global changes since the previous 3rd edition in 2017. These updates include comprehensive revisions to ensure compliance with the latest 2024 SOLAS requirements and acceptance by maritime administrations worldwide.
Notable updates encompass revised sections on extinguishing media, expanded coverage on fire spread and ventilation practices, and updated guidelines on operational responsibilities—see below the latest updates that have been added into thr latest 4th edition SOLAS Fire Training Manual:
Key Changes: 3rd to 4th Edition Fire Training Manual
- Technological Advancements and Global Changes: The manual has been thoroughly updated to reflect the latest technological advancements, evolving shipping practices, and global changes since 2017. This ensures that fire safety provisions remain aligned with current industry standards and best practices.
- Revised Sections on Extinguishing Media: The 4th Edition includes revised sections on extinguishing media, addressing emerging concerns such as the replacement of AFFF foam and mitigation strategies for lithium-ion vehicle fires. These revisions are crucial for keeping abreast of evolving fire suppression techniques.
- Expanded Coverage on Fire Spread, Growth, and Ventilation Practices: Recognising the importance of understanding fire dynamics, the manual now provides expanded coverage on fire spread, growth, and ventilation practices. These updates equip maritime professionals with comprehensive knowledge to effectively manage fire incidents on board.
- Integration of Alarm Monitoring and Control Systems (IAMCS): To enhance fire response capabilities, a new section outlines the functions of Integrated Alarm Monitoring and Control Systems (IAMCS). These systems play a crucial role in early detection and rapid intervention, minimizing the impact of fire emergencies.
- Updated Guidelines on Command, Control, and Fire Team Responsibilities: The 4th Edition incorporates updated and expanded guidelines on command, control, and fire team responsibilities. Clear and well-defined roles ensure efficient coordination during fire emergencies, promoting a swift and organized response.
- Expanded Fire Safety Operational Booklet: An expanded Fire Safety Operational Booklet now includes updates applicable to various vessel types. References to the new Industrial Personnel (IP) Code and SOLAS Chapter XV (effective July 2024) further enhance compliance and safety measures tailored to specific ship categories.
- Customisation for Vessel-Specific Equipment and Procedures: The manual continues to offer provision for customizing procedures to vessel-specific equipment and requirements. This ensures that fire safety protocols are tailored to the unique characteristics of each vessel, optimising safety measures and compliance efforts.
- Comprehensive Coverage of Vessel Types: The 2024 SOLAS Fire Training Manual comprehensively covers various vessel types, including fires in port, dangerous goods handling, passenger vessels, tankers, offshore support vessels, and more. This expansive coverage ensures that the manual remains relevant and effective across diverse maritime operations.
These updates emphasise the evolving landscape of fire safety in marine operations under SOLAS regulations and other maritime Adminstration—since it's official inception in 1914, addressing emerging challenges and technologies. By keeping the manual relevant and effective, maritime professionals can navigate the complexities of fire safety with confidence, safeguarding lives and assets at sea.
Updating from 3rd to 4th Edition SOLAS Fire Training Manual


The revisions in our 4th edition of the SOLAS Fire Training Manual encompass comprehensive updates aimed at addressing the evolving landscape of maritime safety regulations. These revisions include expanded coverage on fire spread and ventilation practices, updated guidelines on operational responsibilities, and the incorporation of new regulations effective from July 2024. This underscores the importance of staying informed and compliant with evolving standards to ensure the safety and security of maritime operations.
Owning the 4th Edition SOLAS Fire Training Manual equips stakeholders with the necessary tools to stay abreast of and comply with the rapidly evolving regulations established by the IMO, MCA, and other maritime organisations or maritime Administrations. By providing up-to-date information and guidance, the manual offers peace of mind to users, enabling them to navigate the complexities of maritime safety regulations with confidence.
Furthermore, it is crucial to recognise that maritime operations face increasingly complex challenges alongside these fast-changing regulations. Therefore, staying updated is essential to ensure the safety of crew, passengers, and vessels alike.
By embracing continuous learning and adaptation, stakeholders can effectively mitigate risks and uphold the highest standards of safety within the maritime industry.
Where Can I Pre-Order the New 4th Edition Fire Training Manual?
The I.C. Brindle SOLAS Fire Training Manual 4th Edition is the latest release in fire training resources. It incorporates recent technological advancements, updates in maritime practices, and global changes since the previous edition in 2017. To pre-order your 4th Ed. Fire Training Manual, please email purchase orders to sales@icbrindle.com, or gives us a call on +44 (0)1202 657814.





